
#Ubuntu sudo password
To set sudo without entering the password is a straightforward way that you don’t need to worry about. You can do it using the etc/sudoers file as we will discuss below. and modify the core sudoers file, but a better option on Ubuntu 22.04 is to add a new. So, instead of entering the password even for a single function, it is better to set sudo without a password. The SSH user requires root privileges and must be able to run sudo. But when you’re the only user of a system and use it as a root user, typing the password multiple times for sudo privileges could irritate you. Type in your current password and hit Enter. Switch to the root user with the command: sudo i. First, open the terminal ( CTRL + ALT + T ). An alternative is to switch to the root user and then run the passwd command to change the root password. It is good to set the password when you have multiple users in a single account. Option 2: Change sudo Password with the passwd Command. It keeps all the records in it about what and when things are done by whom. System administrators can give access to the users to run some specific command or all commands.
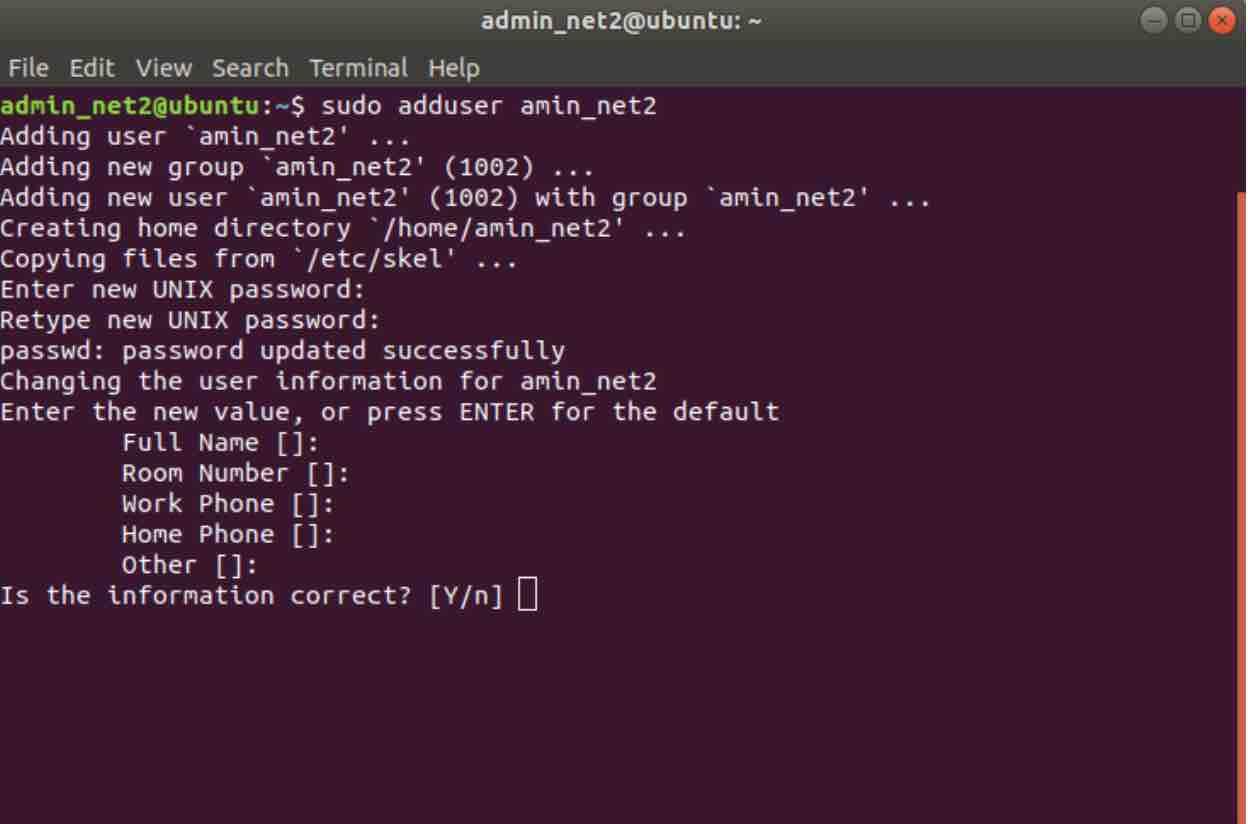
The Sudoers is the administrator’s file used for system configuration. You may verify the creation of the new user by checking the content of the /home directory or grep on the username in /etc/passwd file.When a user executes the command with the sudo privileges, it asks for the password to run it and confirms the user’s request to perform that specific function from the file sudoers. After confirmation, the user will be created successfully. You may enter the details if you want to, but it is not mandatory. Enter the password for the current user (sudo) if necessary, then enter the password for the new account twice and enter additional information as required. It also asks for details for name, phone numbers, and others. With the adduser command, the home directory for the user is also created. Extended security for infrastructure and applications. Kernel Livepatch for 24/7 patching with no downtime. 10 year security maintenance and CVE Patching. Governments and auditors certify Ubuntu for FedRAMP, FISMA and HITECH.
#Ubuntu sudo Patch
Here's a sample screenshot for the creation of a new user named handbook: Patch the full stack, from kernel to library and applications, for CVE compliance. You may also use Ctrl+U Linux shortcut to delete the entire line and start from the beginning. When you type your password, it will be invisible, but you can also use delete or backspace whenever you like. You can read the difference between adduser and useradd here. You can either adduser or useradd command for adding a new user. This is to ensure that only people who are having rights over the system or in charge of protecting the system are creating new users and nobody else. To create a user, one must be a sudoer or a root. Note: Adding a new user will also create a user group named the same as the user in Ubuntu. You add it to the sudoer list in the next step.
Keep in mind that the user will be a regular user when you create it. The root user account in Ubuntu is disabled by default for security reasons, and users are encouraged to perform system administrative tasks using sudo.
If the user that you want to grant sudo access doesn't exist, the first step would be to create that user. Please check the users present on your Linux system.
Let’s now get started on creating a sudo user or sudoer in Linux command line. However, I am not sure if all Linux distributions have a group named sudo. The commands used here are standard Linux commands and these should be installed on most Linux distributions by default. I am using Ubuntu in this tutorial, but the steps mentioned here should apply to Debian and many other Linux distributions as well. That was too short, right? Don't worry! I explain the steps in detail. I'll just show how you can add a sudo user to Ubuntu or Debian. In Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux systems, sudo is practically synonymous with root but in reality, sudo is much more than that.īut I am not going to go into details on sudo here. Furthermore, you can find the Troubleshooting Login Issues section which can answer your unresolved problems and equip you. LoginAsk is here to help you access Ubuntu Add New Sudo User quickly and handle each specific case you encounter. You just add sudo before the command to run it with root privilege. Ubuntu Add New Sudo User will sometimes glitch and take you a long time to try different solutions. You don't need to know the root password or switch to root user. As a sudo user, you can run commands and access files as root user but with your own password.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
